
Endangered Animals
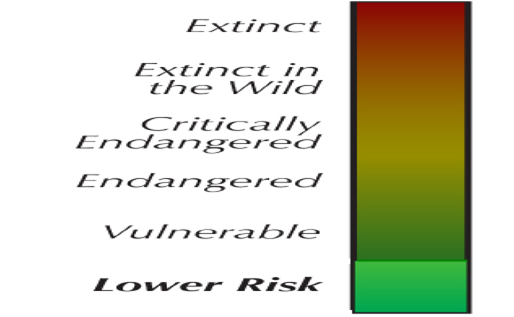
Conservation Meter
• The conservation meter can be found on all animal exhibits at the zoo.
• This meter shows how well an animal population is doing in the wild.
Ways that species become endangered or extinct
• Competition with other species
• Disease
• Predation
• Habitat loss
• Unregulated or illegal killing or collection
• Pesticides and pollution

Extinction
• Extinction is the disappearance brought about by natural or unnatural means of an entire species.
• Some species of plants and animals die out naturally because newer species are more successful at competing for food and living space. Others have become extinct due to changes in the planet or natural disasters.
Saber-toothed Tiger
• The Saber-toothed Tiger, a prehistoric cat, once roamed the earth between California and Argentina.
• It became extinct at the end of the ice age.

Humans a problem?
In today's world, however, species mostly become extinct or are threatened with extinction because of humans. Humans hunt animals, destroy their habitats, and introduce other animals that prey upon the endangered animals or compete for their resources. Among these factors, the greatest threat to plants and animals is habitat destruction
Habitat Destruction
Habitat loss takes several forms:
– Outright loss of areas used by wild species.
– Degradation- for example from vegetation removal and erosion, which deprive native species of food, shelter, and breeding areas.
– Fragmentation- when native species are squeezed onto small patches of undisturbed land because they are surrounded by areas cleared for agriculture and other purposes.
Vegas Valley Leopard Frog
The Vegas Valley leopard frog is extinct due to habitat loss resulting from spring capture and ground water pumping by the growing city of Las Vegas.

Threatened
• Threatened species are any species (including animals, plants, fungi, insects, bugs, etc.) which are vulnerable to extinction in the near
future.
• Threatened species can be grouped into three categories depending on the degree to which they are threatened
Ø Critically endangered
Ø Endangered
Ø Vulnerable
Critically Endangered
Critically endangered is when a species is facing extremely high risk of extinction in the wild in the immediate future.
Red wolves
Red wolves have many problems that threaten their future. The expansion of agriculture, logging and human settlement cleared the forest home of red wolves causing habitat destruction. Between 1900 - 1920 red wolves were hunted because they preyed on cattle this also led to their population decline.


Endangered
• An endangered species is facing a high risk of extinction in the
near future. It means that something is attacking its home, its foodsource, or directly attacking that species.The black and white ruffled lemur, like most animals in Madagascar, are endangered due to habitat destruction.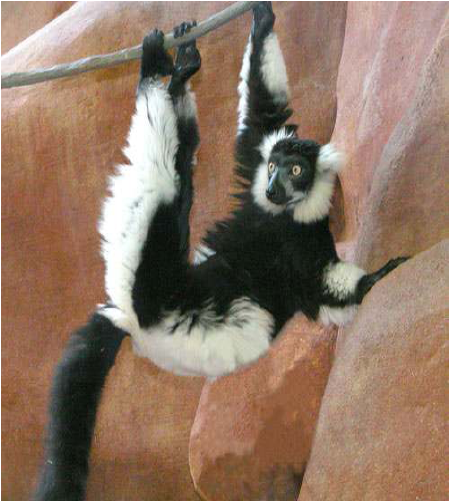 
Vulnerable
A species is considered vulnerable when it is facing a high risk of total destruction in the medium to long term future.Matschie's tree kangaroos are a vulnerable species. They survive only in a small area on the island of Papua New Guinea. Their habitat destruction is being caused by logging, mineral, and oil exploration. Also, hunting by local people is decreasing the number of wild tree kangaroos.

Low Risk
A species is considered at low risk when it has a favorable number of species doing well in the wild.• The Chilean flamingo is considered low risk however its natural habitat is declining and it is a protected species.


• It is estimated that about 125 species of birds and 60 species of mammals have become extinct since 1600.
• Currently, there are approximately 1000-1100 species of birds and mammals that are threatened with extinction.
• If invertebrates and plants are included, the total number of species in imminent danger is around 20,000.
REASONS FOR DEPLETION OF WILD LIFE
1. Absence of shelter to wild animals.
2. Deforestation
3. Destruction of wild plants which affects the survival of wild life
4. Pollution
NECESSITY FOR WILD LIFE CONSERVATION
1. The wild life helps us in maintaining balance of nature.
2. It can increase our foreign exchange if linked with tourism.
3. The preservation of wild life helps to make their study easy.
4. The wild life of India is our cultural asset and had deep rooted effect on Indian art, sculpture and religion.
MODES OF WILD LIFE CONSERVATION
• Protection by law
• Protected species of Indian wild life
• Establishment of Sanctuaries and National park
• Natural habitates of wild life should be carefully protected
• Shooting and hunting of endangered species should be totally banned
• Research on wildlife should be encouraged
• Public should be educate
Please save the wild animals